Phaeophyceae |
Fucales |
Sargassaceae
Environment: milieu / climate zone / تغييرات عمق / distribution range
بوم شناسي
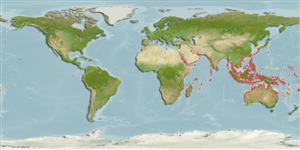
. Tropical
Indian Ocean: from the Arabian Sea, including the Persian Gulf and the Red Sea south to Mauritius, east to India; in the Bay of Bengal, south to Dampier Archipelago, Western Australia, including Andaman and Nicobar Islands; Pacific Ocean: from China going to the South China Sea, south to Queensland, Australia, east to the Samoan Archipelago, including New Caledonia, Solomon Islands and Republic of Palau.
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / سن
بلوغ: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Holdfast small, discoid; stem short, about 5 mm long, cylindrical to slightly compressed, brownish, finely villose, simple or sometimes branched. Primary branches smooth and strongly flattened, especially at basal portions, 3 to 4 mm at broadest portions. Secondary laterals distichous, alternately arranged along primary branches, up to 18 cm long. Leaves of vegetative materials large, linear-lanceolate, up to 7 cm long, 1.2 cm wide, with very short stalks; those of fertile materials much smaller and reduced, especially toward apical portions, linear to linear-lanceolate. Base of leaves acute to cuneate; margin irregularly serrate-dentate; apex mainly obtuse to acute, those of the smaller leaves mainly acute; midrib distinct almost up to apex. Cryptostomata slightly elevated and scattered on blade, those on small leaves at terminal branches with tendency to form rows along both sides of midrib; those on female receptacles more numerous and distinctly elevated, giving the receptacles a lumpy appearance. Vegetative plants with larger vesicles, 1 to 5 mm wide; those of fertile materials smaller and variable in size, the larger ones 4 to 5 mm long and 2 to 3 mm wide, smaller ones 1.5 mm long and 1 mm wide; most vesicles with cylindrical stalks, mainly 1 mm long, those on female plants longer (up to 4 mm) and stalks flattened; apices of vesicles mainly plain or occasionally with teeth or spines. Plants dioecious. Male receptacles paniculate; receptacular branches up to 3 times unequally dichotomously branched, branches terete but highly warty. Female receptacles form dense cymes; receptacular branches simple or shortly branched, almost of same length, apices slightly compressed, margins and tips with few teeth or spines.
Primary branches up to 80 cm in length (Ref. 80758).
Important source of alginate mainly used as emulsifying, stabilizing and gelling agents in food products; contains iodine, protein, vitamin C, and minerals such as Ca, K, Mg, Na, Cu,Zn, S, P, Mn; used as medicine: goiter, glandular troubles, antibacterial, antitumor; source of tannins and phenols; also
used for animal feed and fertilizer (Ref. 80758).
Life cycle and mating behavior
بلوغ | تولید مثل | تخم ریزی | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
مآخذ اصلی
مراجع | هماهنگ كننده | همكاران
Guiry, M.D. and G.M. Guiry 2009 AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. http://www.algaebase.org; searched on 14 April 2009. (مرجع 80701)
وضعيت در فهرست قرمز IUCN
(مرجع 130435: Version 2025-1)
وضعيت از نظر سايتس (مرجع 108899)
Not Evaluated
Not Evaluated
خطر برای انسان ها
استفاده انسانی
ماهي گيري – شيلات: تجاري
| FishSource |
ابزارها
اطلاعات بيشتر
Trophic EcologyFood items (preys)
تركيب غذايي
مصرف غذايي
شکارچیان
Population dynamicsرشد
Max. ages / sizes
Length-weight rel.
Length-length rel.
نوسانات طولی
Mass conversion
فراواني
Life cycleتولید مثل
بلوغ
Fecundity
تخم ریزی
Eggs
نمو تخم
Larvae
PhysiologyOxygen consumption
Human RelatedStamps, coins, misc.
منابع اينترنتي
Estimates based on models